
Comorbid conditions including CKD, diabetes, hypertension, coronary artery disease, heart failure, liver disease, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease are risk factors for AKI.All this compared to those whose serum creatinine levels increased after surgery.Ĭomorbid Conditions and Creatinine Clearance.Finally, the patients with decreases in serum creatinine levels from baseline immediately after surgery were less likely to develop AKI.The strongest predictors of postoperative AKI among clinical risk scores are baseline kidney function and CKD status according to the Creatinine Clearance.In addition, numerous studies derived clinical risk scores of predictors of AKI after cardiac surgery.

Severe AKI requiring RRT occurs in an estimated 1–2% of these patients.The estimated incidence of AKI in cardiac surgery patients is 11–30%.Furthermore, the overall utility of these definitions and staging systems in the clinical assessment and management of patients with AKI remains to be validated.Moreover, these definitions based exclusively upon the serum Creatinine Clearance and urine output and are used primarily to identify patients with AKI in epidemiologic and outcome studies.Several consensus definitions of AKI developed to provide a uniform definition of AKI.Additionally, associated with increased morbidity and mortality.The term AKI has largely replaced acute renal failure (ARF), reflecting the recognition that smaller decrements in kidney function that do not result in overt organ failure are of substantial clinical relevance.This is resulting in the retention of urea and other nitrogenous waste products and the dysregulation of extracellular volume and electrolytes.Acute kidney injury (AKI) refers to an abrupt decrease in kidney function.Drug Dosing According to Creatinine Clearance Calculation.Definition of Creatinine Clearance & formula.Medications affected the AKI and Creatinine Clearance.Fluid resuscitation in AKI and Creatinine Clearance.Serum Creatinine Level and Creatinine Clearance.Diagnosis of AKI and Creatinine Clearance.Classification of Causes of AKI and Creatinine Clearance.Comorbid Conditions and Creatinine Clearance.

The following table introduces the various formulas used to determine body surface area: AuthorĠ.0003207 x (Height in cm) 0.3 x (Weight in grams) (0.7285 - ( 0.0188 x Log(Weight))Ġ.007184 x (Height in cm) 0.725 x (Weight in kg) 0.425Ġ.0235 x (Height in cm) 0.42246 x (Weight in kg) 0.51456Ġ.024265 x (Height in cm) 0.3964 x (Weight in kg) 0. In case the serum creatinine is given in mg/dL, the conversion from mg/dL to µmol/L is: 1 mg/dL = 88.4 µmol/L. ■ Serum creatinine is expressed in µmol/L. ■ BSA is calculated via Boyd’s, DuBois’s, Gehan & George’s, Haycock’s or Mosteller’s formula.
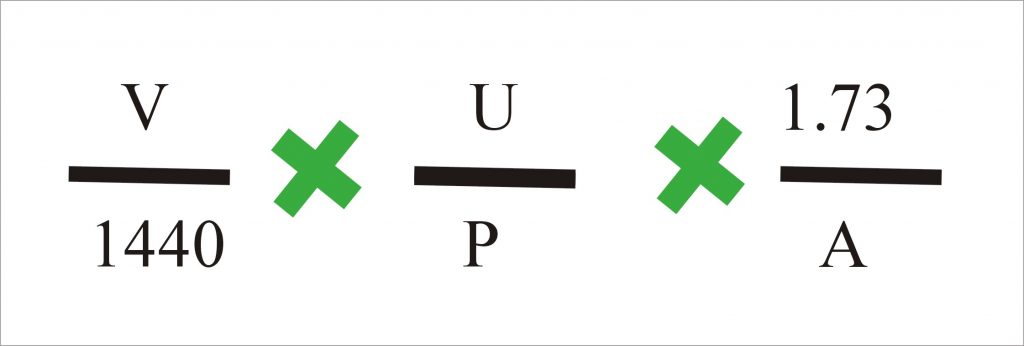
■ Gender value is 0 for men and 1 for women. The estimated creatinine clearance rate (eCCr) based on the 1973 equation by Jelliffe is:ĮCCr = / (Serum creatinine in µmol/L x 0.0113) ■ Body surface area (used in the CrCl equation) The CrCl calculator also displays other indicators of body health: Serum creatinine can be input in either mg/dL or µmol/L. The above calculator is flexible in terms of the measurement system used and accepts both English and Metric determinations. The formula also accounts for patient age, gender, height and weight. This can be then input in the Jelliffe equation to retrieve the creatinine clearance rate which is an indicator of renal function. Serum creatinine is a laboratory determination that is easy to obtain through a blood test.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
